Introduction
Typhoid fever, caused by the bacterium Salmonella typhi, is a serious infectious disease that poses a significant health risk in various regions, including South Africa. The importance of understanding typhoid fever has grown recently due to reported increases in cases, particularly among vulnerable populations. With a country grappling with healthcare challenges, keeping informed about typhoid fever can contribute to community health and safety.
Current Situation and Statistics
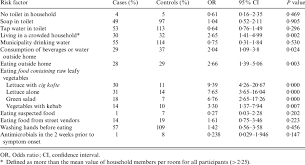
Recent health reports indicate a resurgence of typhoid fever cases across South Africa, with the National Institute for Communicable Diseases (NICD) noting an increase in infections over the past year. Data shows a correlation between typhoid outbreaks and inadequate sanitation, particularly in areas with poor access to clean water. The disease is primarily transmitted through food and water contaminated with the feces of an infected person, making hygiene and sanitation critical factors in its spread.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Common symptoms of typhoid fever include persistent fever, abdominal pain, weakness, and loss of appetite. In some cases, patients may experience gastrointestinal bleeding. Due to the overlap of these symptoms with other diseases, accurate diagnosis often requires specific blood or stool tests. Early recognition and treatment are crucial to preventing severe complications associated with the disease.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing typhoid fever largely revolves around improving sanitation and hygiene practices. Health officials recommend ensuring access to clean drinking water, improving sanitation facilities, and promoting handwashing with soap, particularly before meals and after using the toilet. Vaccination is also available and recommended for at-risk individuals, such as those traveling to endemic areas.
Conclusion
Typhoid fever remains a public health concern in South Africa. With the rise in reported cases, awareness is key to prevention and control. Continuous education on hygiene practices, enhancing water and sanitation infrastructure, and increasing vaccination uptake can significantly reduce the incidence of typhoid fever. It is essential for communities and officials to work together to tackle this preventable disease effectively. The collective efforts of society can ensure safety and health for all, underscoring the importance of vigilant health safeguarding measures.